Soil health
Soil health is a topic of discussion by microbiologists and agronomists alike.
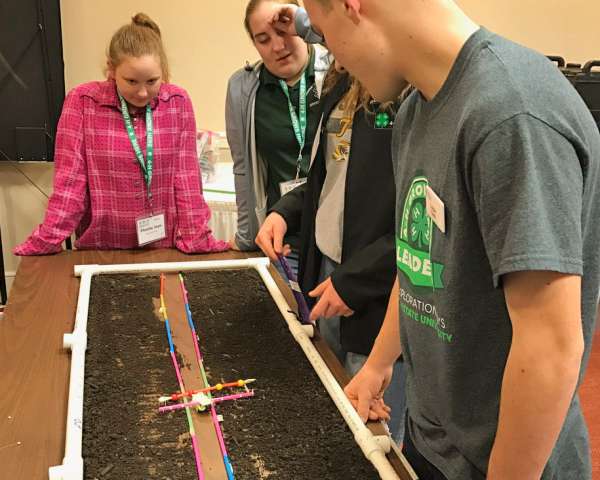
Soil is home to biotic factors: microbes, insects, spiders, worms; and abiotic factors: minerals, nutrients, water and air. The soil ecosystem is more important than ever in determining the yield of crops as well as the nutrition content of the food that we eat. These materials consider the aspects of soil health and how food production systems can maintain and bolster soil health.






















Share this