A closer look at insects
Lessons
# How do insects impact agriculture
Students classify and identify insects that impact soybeans.
Files
# Bioinformatics of insects
Students explore insect diversity in a field through DNA analysis.
Files
-
Bug sequences
-
Bug BLASTer: Exploring insect diversity in the soybean field using DNA sequence analysis (student)
-
Bug BLASTer: Exploring insect diversity in the soybean field using DNA sequence analysis (teacher)
-
Bug BLASTer: Exploring insect diversity in the soybean field using DNA sequence analysis (student)
# Microbes in insects
Students collect and stain microbes for identification and test for antibiotic susceptibility.
Files
Teacher background
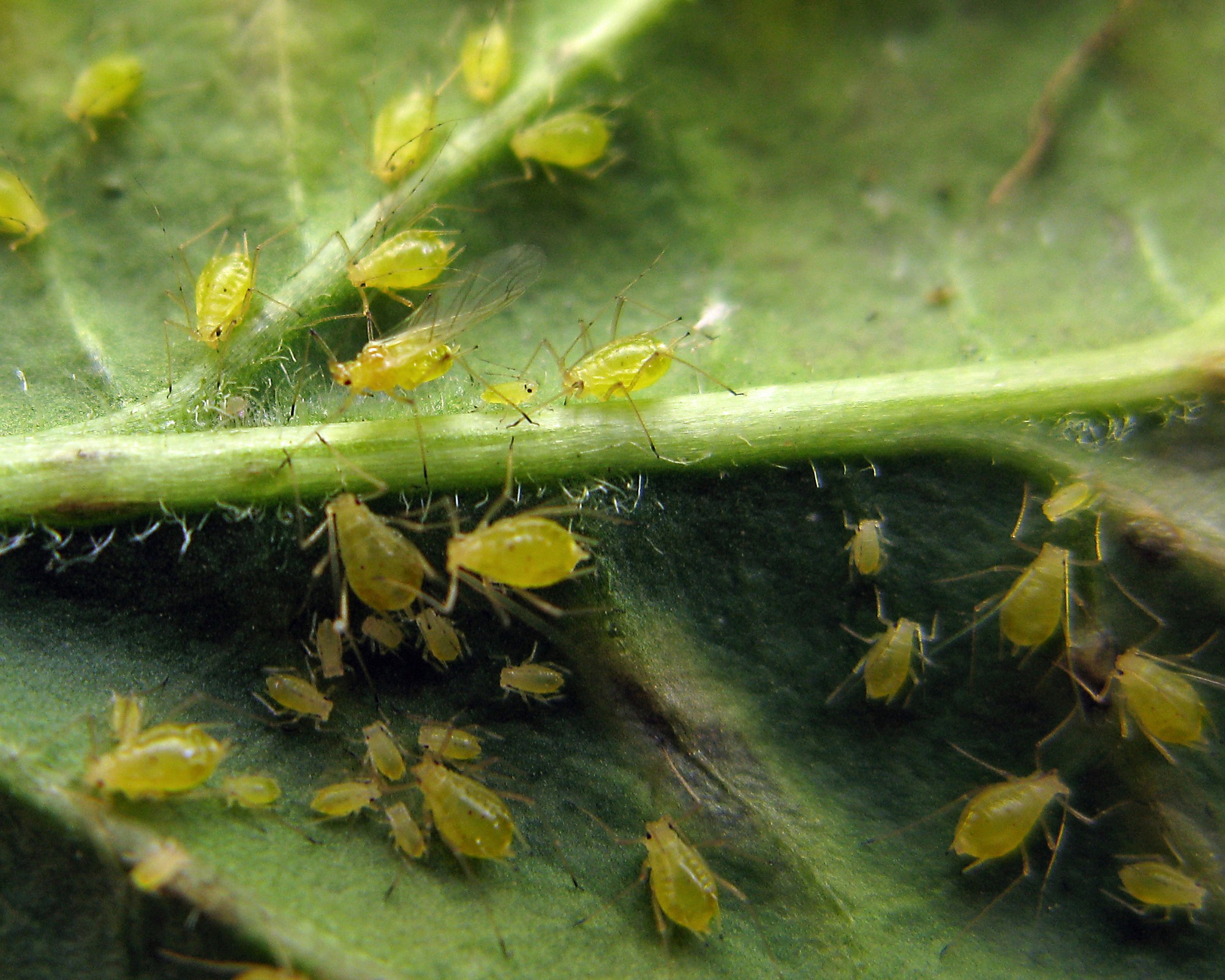
Insects are the most diverse group of organisms on the planet. About nine hundred thousand different kinds of living insects are known. This is approximately 80 percent of the world’s species.
Insects greatly impact US agriculture. Between 20% to 40% of global crop production is lost annually to insect damage. Each year, plant diseases cost the global economy around $220 billion, and invasive insects around $70 billion.
Insecticide application may be required at any time throughout the development of the crop. At planting time, seed treatments protect against seed maggots. Treatment following emergence may control overwintering bean leaf beetles. Up to bloom, soybeans can tolerate up to 40 percent defoliation without an economic loss in yield. However, from bloom to pod-fill, soybeans are more susceptible. Defoliation should not be allowed to exceed 15 percent during that time. Once pods have set, treatment is needed when bean leaf beetle affects 10% or more of the pods. Farmers must scout the fields throughout the growing season.
There are also many beneficial insects in the field. They may be useful for a method called conservation biological control. This procedure is a science-based pest management strategy that integrates beneficial insects back into cropping systems for natural pest control. It can reduce and in some cases eliminate the need for pesticides.
But what if some of these insects could provide researchers with antibiotic or antimicrobial substances to use? Even destructive insects may have antimicrobial metabolites that protect them from bacteria. Researchers are looking for these metabolites to potentially develop new antibiotics for humans.
See Seeds of Change to learn more about insect microbiome prospecting.

Next gen science standards
Science and engineering practices
- Asking questions (for science) and defining problems (for engineering)
- Analyzing and interpreting data
- Using mathematics and computational thinking
- Constructing explanations (for science) and designing solutions (for engineering)
- Engaging in argument from evidence
- Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information
Crosscutting concepts
- Cause and effect
- Structure and function
- Stability and change
Disciplinary core ideas/content
- LS1A Structure and Function
- LS1B Growth and development of organisms
- LS1C Organization for matter and energy flow in organisms
- LS1D Information processing
- LS2A Interdependent relationships in ecosystems
- LS2D Social interactions and group behavior
- LS4C Adaptation
- ETS2A Interdependence of science, engineering and technology






Share this