Are you sterile? Using sterile technique to tissue culture plants
Lessons
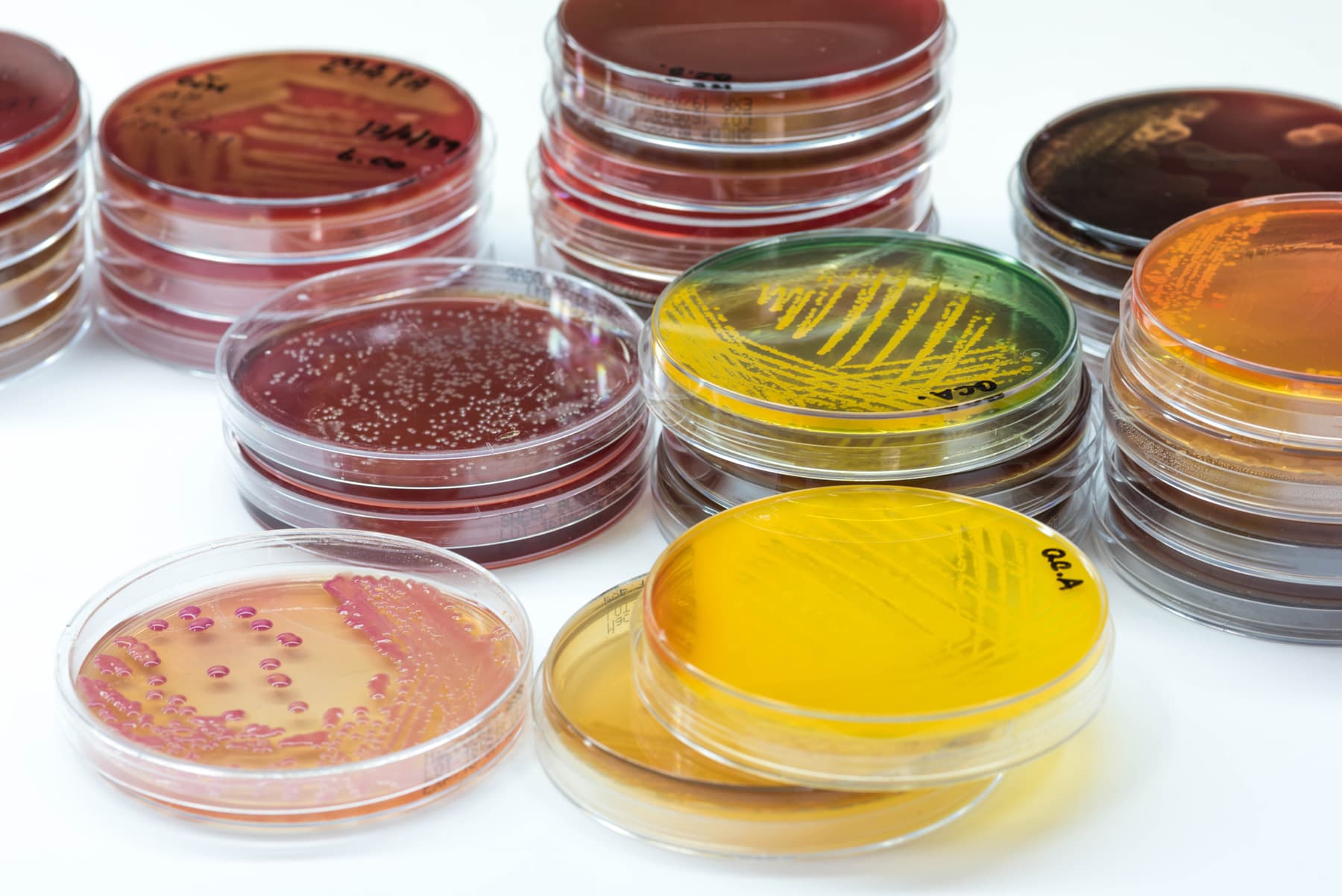
# Compare Leaf Sterilization to a Control
Collect a leaf from a plant. Compare the microbial growth from an untreated leaf to the microbial growth from a leaf treated with 70% isopropyl alcohol.
Files
# Comparison of IVC Treatments
Prepare various media treatments to prevent contamination of IVC and properly record the preparation information in a Medium Preparation log. Test various media treatments to compare their effectiveness at preventing contamination. Present findings in lab notebooks using the IVC Lab Rubric.
Files
Teacher background
In vitro collecting allows for the potential to conserve crops and wild or endangered species. The level of contamination must be controlled, which permits successful growth of any in vitro collected germplasm. This technique is also called micropropagation, and produces clones of the tissue collected. It has proven beneficial in producing disease-free plants and increasing plant yields in developing countries. A sterile work environment, a greenhouse, and training in biotechnology skills are required.
Biotechnology has a wide variety of career opportunities ranging from sales and marketing, to research and development, manufacturing and quality control and assurance. The total number of biotechnology companies is increasing, and employment in the biotechnology field continues to grow as well.
“Currently, there are more than 250 biotechnology health care products and vaccines available to patients, many for previously untreatable diseases. More than 13.3 million farmers around the world use agricultural biotechnology to increase yields, prevent damage from insects and pests, and reduce farming’s impact on the environment. And more than 50 biorefineries are being built across North America to test and refine technologies to produce biofuels and chemicals from renewable biomass, which can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.” Biotechnology Innovation Organization
Next gen science standards
Science and engineering practices
- Asking questions (for science) and defining problems (for engineering)
- Analyzing and interpreting data
- Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information
Crosscutting concepts
- Cause and effect
Disciplinary core ideas/content
- ESS3A Natural resources
- ESS3C Human impacts on Earth systems
- LS1B Growth and development of organisms
- LS2A Interdependent relationships in ecosystems
- LS4C Adaptation
- LS4D Biodiversity and humans
- ETS1B Developing possible solutions





Share this