Be a food scientist
Lessons
# Introduction to Food Science
Engage students by showing videos for more information on food safety laws.
Files
# Food Safety
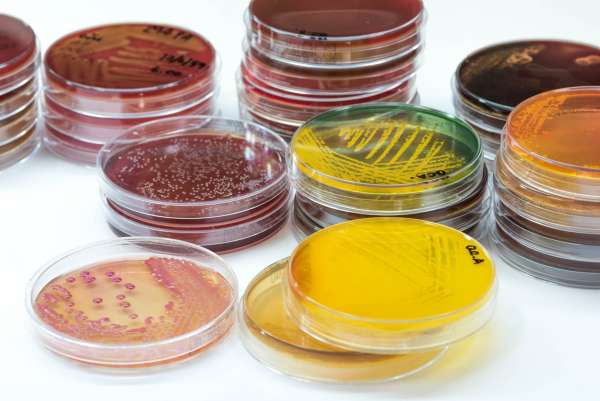
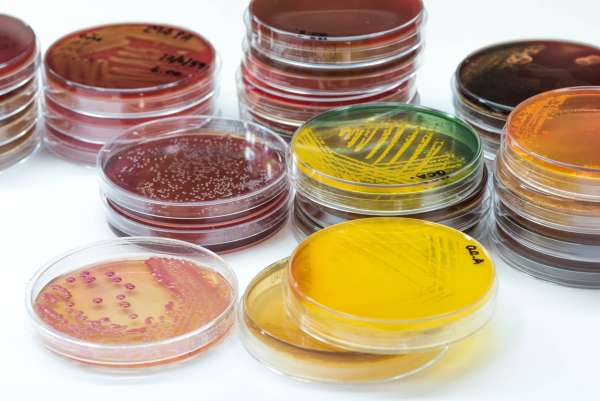
Illustrate the importance of food safety techniques to ensure food quality by creating a survey from the questions suggested and conduct it with a class or school; preparing agar plates using aseptic preparation methods; investigating the effectiveness of various types of hand cleaners to determine if they have antimicrobial action, monitoring cooking stations by following this standardized test to ensure the safety and quality of food production; determining the effect of temperature on bacterial growth.
Files
# What is your Protein IQ? cookbook
Create a cookbook of recipes using proper cooking techniques to share with a larger audience using the assignment description, the rubric, a template and an example of one Standard Laboratory Operating Procedure (SLOP) recipe.
Files
# Biomolecules Information
Fill in the information about biomolecules from the video Macromolecules Gone Wild. Students may check their answers using the Biomolecules Chart Key.
Files
# Testing for Biomolecules
Test soy milk and student-created individual recipes, using macromolecule tests.
Files
Teacher background
Food science is a growing career field. The average supermarket carries more than 20,000 items, most of which were developed into safe, affordable, and tasty products by food scientists. Currently, the demand for Food Science graduates exceeds the number of degrees awarded.
This unit focuses on the biotechnology, biology and chemistry of food and employs techniques used by food scientists as they develop new food products. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for protecting the public health by assuring the safety, efficacy and security our nation’s food supply. Prevention of issues that can cause illness is the focus of the new FDA Food Safety Law.
Next gen science standards
Science and engineering practices
- Analyzing and interpreting data
- Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information
Crosscutting concepts
- Scale, proportion, and quantity
Disciplinary core ideas/content
- ESS1A The universe and its stars
- LS1C Organization for matter and energy flow in organisms
- LS2B Cycles of matter and energy transfer in ecosystems
- PS1B Chemical reactions
- PS4B Electromagnetic radiation
- PS4C Information technologies and instrumentation




Share this